This Site Is A Participant In The Amazon Services LLC Associates Program. We may earn money or products from Amazon or the companies mentioned in this post.
Azelaic acid is a naturally occurring substance found in whole-grain cereals and animal products. It has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and keratolytic properties. Azelaic acid is used as a topical treatment for acne vulgaris and rosacea.
When applied to the skin, azelaic acid helps to reduce redness and inflammation. Additionally, it can help to unplug blocked pores and kill acne-causing bacteria.
Azelaic acid is a natural substance found in wheat, rye, and barley. It’s also produced by bacteria that live on our skin. Azelaic acid has many benefits for the skin.
It’s an anti-inflammatory, so it can help reduce redness and swelling. It’s also an antioxidant, so it can help protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals. Azelaic acid can also help to unclog pores and clear up acne.
There are many ways to incorporate azelaic acid into your skincare routine. You can find products that contain azelaic acid at most drugstores or online. Look for cleansers, toners, moisturizers, serums, or spot treatments that contain azelaic acid as an active ingredient.
Start with once or twice daily use and increase as tolerated.
If you have sensitive skin, you may want to try a product that contains azelaic acid in a lower concentration.
AZELAIC ACID – 5 Things I Wish I Had Known | How To Use Azelaic Acid
What Does Azelaic Acid Do for Face?
Azelaic acid is a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid that has many benefits for the skin. It is found in wheat, barley, and rye and has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. Azelaic acid helps to reduce the appearance of acne by killing the bacteria that cause acne and by reducing inflammation.
It also helps to lighten hyperpigmentation and Evens out skin tone.
Can I Get a Facial While Using Azelaic Acid?
Azelaic acid is a naturally occurring compound found in grains like wheat and barley. It’s also the active ingredient in many over-the-counter acne treatments. Azelaic acid can be very effective at treating acne, but it can also cause some side effects like dryness, redness, and irritation.
So, if you’re thinking about getting a facial while using azelaic acid, it’s important to talk to your dermatologist first. They can help you figure out if it’s safe for you and whether or not you’ll need to adjust your skincare routine.
How Often Should I Use Azelaic Acid on My Face?
Azelaic acid is a naturally occurring compound found in grains like wheat and barley. It’s also present in the skin of certain fruits like apples and pears. Azelaic acid has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, which makes it an effective acne treatment.
There is no definitive answer to how often you should use azelaic acid on your face. However, most experts recommend using it two to three times per day. If you have sensitive skin, start by using it once per day and increase frequency as tolerated.
You can apply azelaic acid to your entire face or just target problem areas.
What is Azelaic Acid Good for Skin?
Azelaic acid is a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid that possesses many benefits for the skin. When applied topically, azelaic acid can help to brighten the complexion and even out skin tone by reducing the visibility of blemishes, pigmentation irregularities and inflammation. Additionally, azelaic acid has antimicrobial properties which make it an effective acne-fighting ingredient.
By unclogging pores and killing bacteria, azelaic acid can help to clear up existing breakouts and prevent future ones from forming.
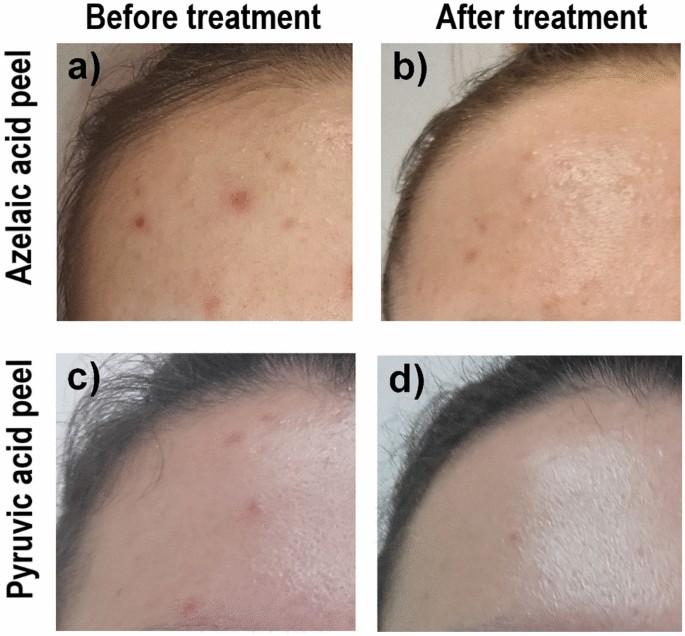
Credit: www.nature.com
Azelaic Acid Benefits
Azelaic acid is a natural substance found in whole grains and animal products. It has many benefits for the skin, including the ability to treat acne, rosacea, and other inflammatory skin conditions. Azelaic acid also has anti-aging properties, making it a popular ingredient in skincare products.
In addition to its benefits for the skin, azelaic acid also has antimicrobial and antioxidant properties.
Best Azelaic Acid Products
Azelaic acid is a natural substance found in wheat and barley. It’s also produced by certain bacteria that live on our skin. Azelaic acid is an effective ingredient in many over-the-counter skincare products for treating acne, rosacea, and hyperpigmentation.
If you’re looking for an alternative to conventional acne treatments like benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid, azelaic acid may be worth trying. Several studies have shown that azelaic acid can effectively reduce the number of pimples and promote healing of existing blemishes.
When shopping for azelaic acid products, look for those that are formulated with 10-15% concentration of the active ingredient.
Be sure to read the label carefully to make sure the product is appropriate for your skin type. Those with sensitive skin may want to start with a lower concentration product and work up to a higher concentration if needed.
As with any new skincare product, it’s always best to test a small area first before applying it to your entire face.
Start by cleansing your face and then applying a pea-sized amount of azelaic acid cream or gel evenly over the affected areas. Use once or twice daily as tolerated. You should begin seeing results within 4-6 weeks of regular use.
Azelaic Acid the Ordinary
Azelaic acid is a multi-functional ingredient that offers several benefits for the skin. These benefits include brightening the skin, evening out the skin tone, improving the appearance of acne and rosacea, and reducing inflammation. The Ordinary’s azelaic acid suspension 10% is a light-textured cream that is perfect for those with sensitive skin.
This product has a high concentration of azelaic acid, which makes it very effective at treating various skin concerns.
Conclusion
Azelaic acid is a natural substance that can be found in wheat, barley, and rye. It’s also produced by yeast that lives on our skin. Azelaic acid has many benefits for the skin, including treating acne, reducing redness and inflammation, evening out skin tone, and fading pigmentation.





