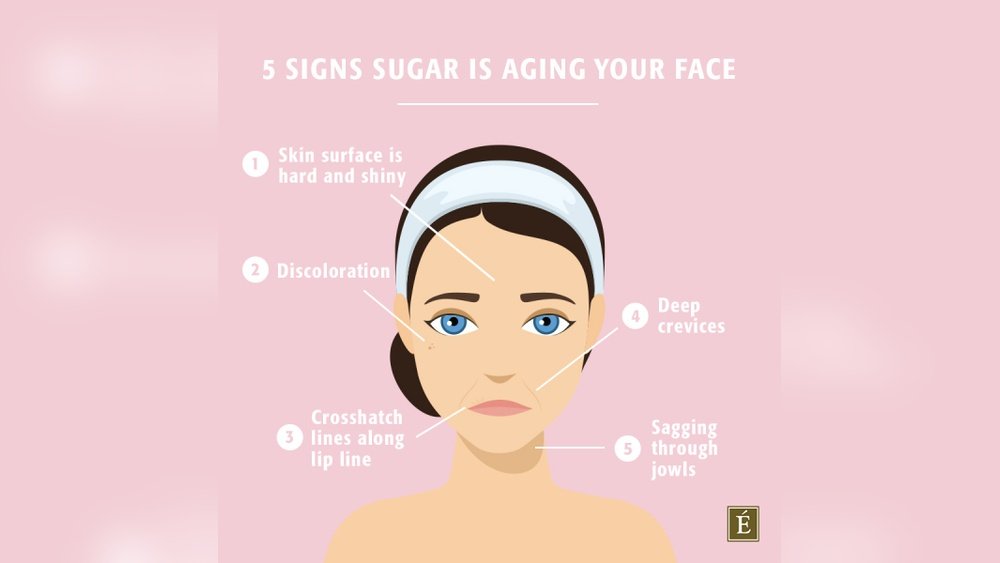
Have you ever wondered why your skin seems to lose its glow or why those fine lines keep appearing faster than you’d like? What if the sweet treats you enjoy daily are secretly speeding up your facial aging?
Sugar isn’t just empty calories—it has a powerful impact on your skin’s health and appearance. From causing wrinkles to making your skin sag, sugar can do more harm than you realize. But don’t worry, understanding how sugar affects your skin puts you in control.
Keep reading to discover the surprising ways sugar ages your face and simple steps you can take right now to keep your skin looking youthful and radiant. Your skin’s future depends on what you do today!
Credit: www.unitypoint.org
Sugar And Skin Aging
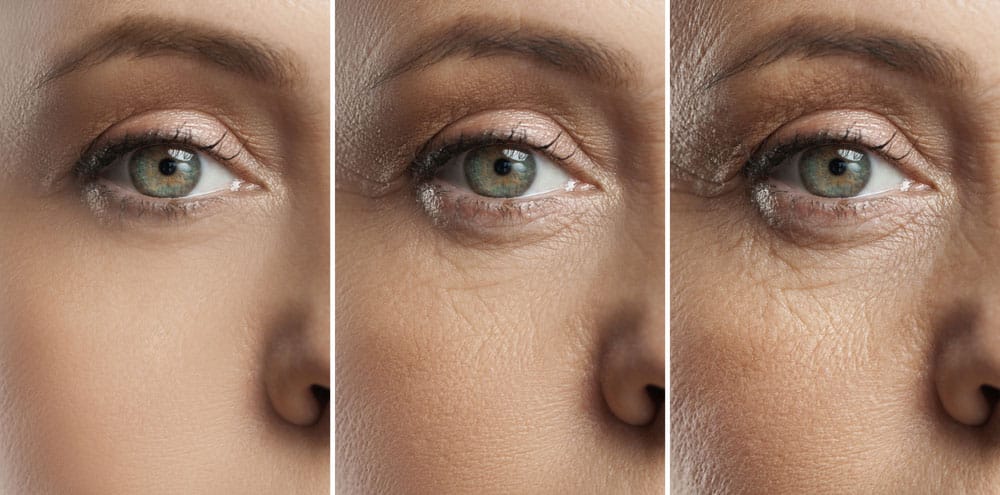
Sugar plays a major role in skin aging. It causes damage at the cellular level and speeds up visible aging signs. The process of sugar reacting with skin proteins harms the skin’s structure.
Understanding sugar’s impact helps protect your skin from early wrinkles and dullness. This section explains how sugar affects your skin and what happens inside.
Glycation happens when sugar molecules bind to collagen and elastin. These proteins keep skin firm and elastic. The bond creates harmful compounds called Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs). AGEs stiffen and weaken the skin.
As a result, skin loses its smoothness and starts to sag. Wrinkles become deeper and more visible. Glycation stops the natural repair of skin proteins, speeding up aging.
Inflammation Caused By Sugar
Eating a lot of sugar triggers inflammation in the body. Inflamed skin looks red, dull, and tired. Chronic inflammation harms skin cells and slows down healing. It can also worsen acne and other skin problems.
Inflammation from sugar makes dark spots and uneven skin tone more common. It reduces the skin’s natural glow and vitality.
Effect On Collagen And Elastin
Collagen and elastin are vital for youthful skin. Sugar damages these proteins by causing cross-links that block their repair. This leads to weaker skin that loses firmness over time. The skin becomes loose and develops fine lines.
The loss of collagen and elastin due to sugar intake speeds up the appearance of aging signs. Healthy skin depends on protecting these proteins from damage.
Accelerated Aging At The Dna Level
Sugar also affects the skin at the DNA level. It speeds up telomere shortening, which is linked to aging. Telomeres protect DNA, but they shrink as we age. Faster shortening means quicker skin aging.
This effect contributes to weaker cell renewal and premature skin aging. Reducing sugar helps slow down this process.

Credit: cathe.com
Glycation And Skin Damage
Glycation is a natural process where sugar molecules bind to proteins in the body. In the skin, this reaction damages collagen and elastin. These two proteins keep skin firm and elastic. When sugar attaches to them, it forms harmful molecules called Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs).
AGEs cause the skin to lose its strength and flexibility. This leads to wrinkles, sagging, and dullness. Glycation also speeds up the aging process by reducing the skin’s ability to repair itself. It weakens the skin’s structure, making it look older faster.
What Is Glycation?
Glycation happens when sugar sticks to proteins or fats. It creates AGEs, which harm skin cells. These molecules build up over time and cause stiffness in collagen and elastin. The skin loses its smooth texture and looks rough.
How Ages Affect Skin Health
AGEs make collagen and elastin stiff and fragile. This prevents the skin from bouncing back. The skin becomes less firm and develops fine lines. AGEs also trigger inflammation, which damages skin further. Inflammation can cause redness and dark spots.
The Role Of Sugar In Glycation
Eating too much sugar increases glycation in the skin. High sugar levels mean more AGEs form. This speeds up skin aging and damage. Sugar also causes inflammation, worsening skin problems like acne and discoloration.
Preventing Glycation Damage
Reducing sugar intake helps slow down glycation. Choosing fresh fruits and vegetables supports skin health. Antioxidants in these foods fight free radicals caused by AGEs. Drinking water and using gentle skincare also protect skin structure.
Inflammation And Dark Spots
Inflammation plays a crucial role in how sugar affects facial aging. Eating too much sugar triggers inflammation inside the body. This inflammation can cause skin problems, including dark spots.
Dark spots appear when the skin produces too much melanin. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its color. Inflammation from sugar causes the skin to overproduce melanin. This makes dark spots more visible and uneven in tone.
Inflammation also damages collagen and elastin. These proteins keep skin firm and smooth. When damaged, skin loses its elasticity and looks older. Sugar speeds up this damage through a process called glycation.
How Sugar Causes Inflammation In The Skin
Sugar increases the production of harmful molecules called advanced glycation end products (AGEs). AGEs cause inflammation by damaging skin cells. This inflammation weakens the skin’s natural barrier. It makes skin more prone to redness, irritation, and dark spots.
The Link Between Inflammation And Dark Spots
When skin is inflamed, it signals cells to produce more melanin. This response is the body’s way to protect damaged skin from further harm. The result is hyperpigmentation or dark spots. These spots can become darker and more widespread with constant inflammation.
Ways To Reduce Inflammation And Dark Spots
Cutting back on sugar helps reduce inflammation significantly. Eating foods rich in antioxidants supports skin healing. Antioxidants fight free radicals that worsen inflammation. Staying hydrated and using gentle skincare can also calm irritated skin.
Sugar’s Effect On Collagen And Elastin
Sugar affects the skin by damaging two key proteins: collagen and elastin. These proteins keep skin firm and elastic. Without them, skin loses its strength and starts to sag. The process that causes this damage is called glycation.
Glycation happens when sugar molecules attach to collagen and elastin. This creates harmful substances called Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs). AGEs make collagen and elastin stiff and weak. This stiffness leads to wrinkles and less flexible skin.
How Glycation Harms Collagen And Elastin
Sugar molecules bind to collagen and elastin fibers. This binding forms AGEs that change the proteins’ structure. Collagen becomes brittle, and elastin loses its stretch. The skin can no longer bounce back from movements like smiling or frowning. This causes fine lines and deep wrinkles.
Reduced Repair Of Skin Proteins
AGEs block the natural repair process of collagen and elastin. Damaged proteins stay in the skin longer. Over time, this buildup causes skin to sag and look older. The body struggles to replace healthy collagen and elastin fast enough.
Inflammation And Its Role In Skin Aging
High sugar intake triggers inflammation in the body. Inflammation breaks down collagen and elastin faster. It also slows down their production. This creates a cycle where skin ages quicker and looks dull. Inflammation can worsen wrinkles and cause redness.
Reducing Sugar For Better Skin
Reducing sugar intake plays a key role in improving skin health. Sugar speeds up skin aging by damaging collagen and elastin. These proteins keep skin firm and smooth. Cutting down on sugar helps maintain skin elasticity and glow.
Less sugar also means less inflammation. Inflammation causes redness, dullness, and dark spots. Reducing sugar can calm these skin issues. It supports clearer, brighter skin over time.
How Cutting Sugar Protects Collagen
Sugar binds to collagen and elastin, creating harmful compounds called AGEs. AGEs stiffen skin fibers and stop repair. Reducing sugar lowers AGE formation. This helps collagen stay strong and skin firm.
Lowering Inflammation For Clearer Skin
High sugar intake triggers inflammation inside the body. This shows up on skin as redness and acne. Reducing sugar calms inflammation. It helps skin heal and reduces breakouts.
Tips To Reduce Sugar For Better Skin
Start by avoiding sugary drinks and snacks. Choose water and fresh fruits instead. Check labels for hidden sugars in processed foods. Focus on whole foods like vegetables, nuts, and lean proteins. Small changes add up to big skin benefits.

Credit: eminenceorganics.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Cutting Out Sugar Reverse Aging?
Cutting out sugar can’t fully reverse aging but slows it by reducing inflammation and glycation. This improves skin firmness and reduces wrinkles.
Does Sugar Increase Skin Aging?
Yes, high sugar intake speeds up skin aging by damaging collagen and elastin through glycation. It causes wrinkles, sagging, inflammation, and dark spots. Reducing sugar helps maintain skin firmness and slows aging signs.
What Happens To Your Face When You Stop Eating Sugar?
Stopping sugar intake reduces inflammation and glycation, improving skin firmness and reducing wrinkles, acne, and dark spots. Your face looks clearer, more youthful, and less dull. Collagen and elastin repair better, slowing visible aging signs and promoting healthier, glowing skin.
What Does A Sugar Face Look Like?
A sugar face shows wrinkles, sagging, dullness, acne, and dark spots. High sugar causes collagen damage and inflammation, aging skin faster.
How Does Sugar Affect Facial Skin Aging?
Sugar causes glycation, damaging collagen and elastin, which leads to wrinkles and sagging skin.
Can Cutting Sugar Slow Down Skin Aging?
Yes, reducing sugar lowers inflammation and helps slow visible signs of aging on the skin.
Conclusion
Sugar harms skin by breaking down collagen and elastin. This causes wrinkles, sagging, and dullness. It also triggers inflammation, worsening dark spots and acne. Reducing sugar intake can help slow these effects. Eating antioxidant-rich foods supports skin health and repair.
Managing blood sugar keeps skin firmer and more youthful. Small changes in diet make a noticeable difference. Protect your skin by choosing healthy foods every day. Your skin will thank you with a fresher, brighter look. Aging gracefully is easier when sugar is kept in check.
 Skip to content
Skip to content