Have you ever noticed your skin looking dull, slow to heal, or suddenly more irritated than usual? What if the root cause isn’t just surface-level but linked to something your body desperately needs—magnesium?
This essential mineral plays a crucial role in keeping your skin healthy, vibrant, and resilient. When your body lacks magnesium, your skin can suffer in many ways, from thinning and discoloration to stubborn acne and inflammatory conditions like eczema. Understanding how magnesium deficiency affects your skin is the first step to reclaiming your natural glow and preventing long-term damage.
Keep reading to discover how this hidden deficiency might be impacting your skin and what you can do to restore balance and health.
Credit: www.geneticlifehacks.com
Magnesium And Skin Health
Magnesium plays a vital role in keeping skin healthy and strong. It supports many processes that help skin cells grow and repair. Without enough magnesium, skin can become weak and prone to damage.
This mineral helps control inflammation, which is important for preventing skin problems. Low magnesium can lead to irritated, red, or dry skin. It also affects how quickly wounds heal and how the skin fights infections.
Magnesium Supports Skin Cell Regeneration
Magnesium provides energy for skin cells to renew themselves. Cells need this energy to repair damage and maintain a smooth surface. A lack of magnesium slows down this process. This leads to thin, fragile skin that heals slowly.
Magnesium Reduces Skin Inflammation
Inflammation causes redness and swelling in the skin. Magnesium helps calm this response. Low levels of magnesium can trigger more inflammation. This worsens conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and acne. Keeping magnesium balanced helps reduce flare-ups.
Magnesium Helps Manage Acne And Allergies
Acne often results from inflammation and clogged pores. Magnesium can help lower inflammation and improve skin’s appearance. It may also reduce allergy symptoms by calming irritated skin. Some studies show magnesium’s role in easing skin allergies and sensitivity.
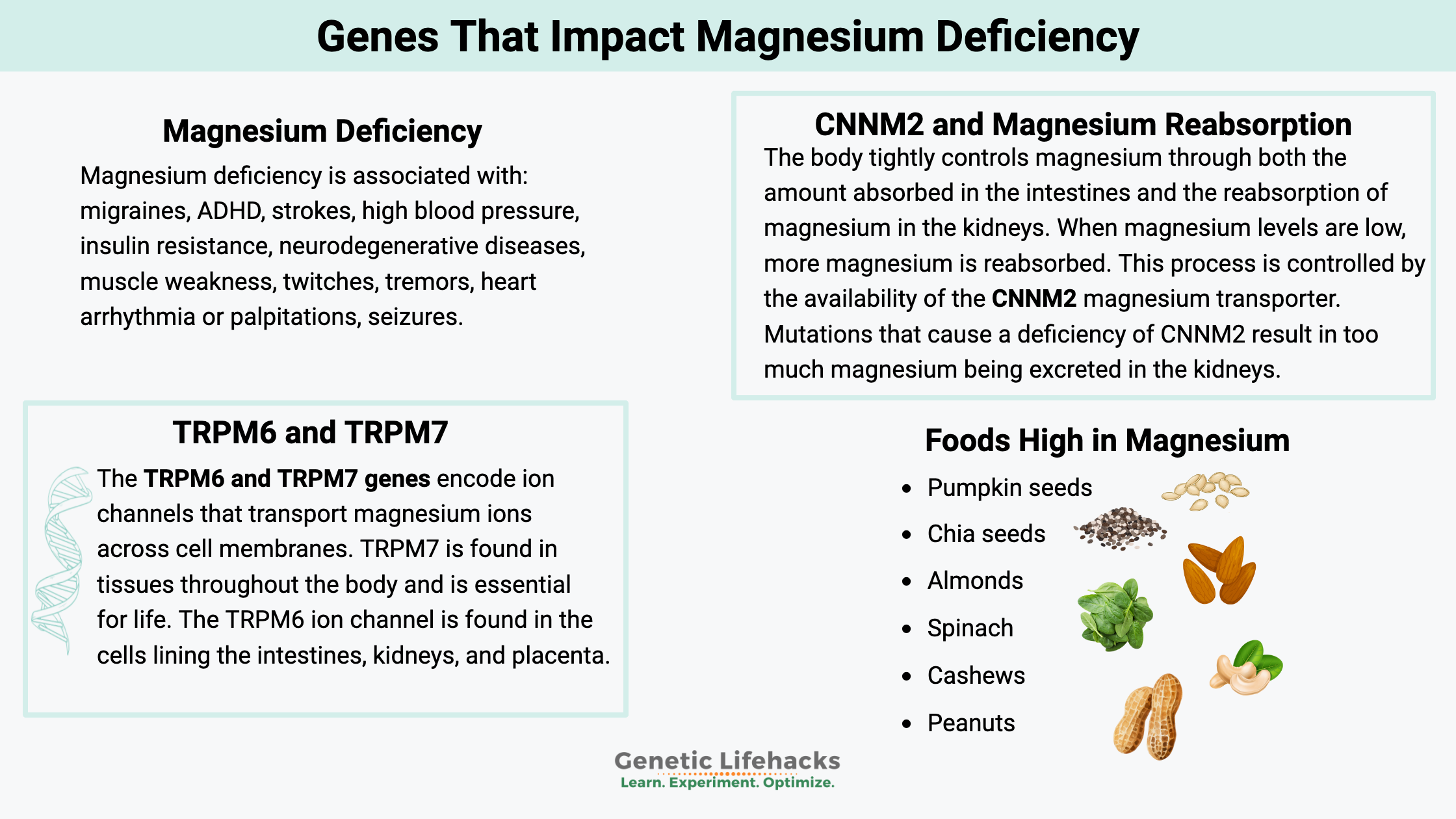
Sources Of Magnesium For Healthy Skin
Eating foods rich in magnesium is the best way to support skin health. Nuts, seeds, green leafy vegetables, and whole grains are good sources. Supplements may help if diet alone is not enough. Consult a doctor before starting supplements.
Topical magnesium, like bath salts, may soothe the skin but does not fix deficiency. The skin absorbs only small amounts, so diet remains key for overall health.
Effects Of Deficiency On Skin
Magnesium deficiency affects the skin in several important ways. This vital mineral supports many skin functions, so low levels can cause noticeable problems. The skin may become weak, slow to heal, and more prone to irritation. Understanding these effects helps reveal why magnesium is essential for healthy skin.
Cell Function And Regeneration
Magnesium is key for skin cell energy and repair. Without enough magnesium, cells struggle to regenerate properly. This leads to thinning skin and slower wound healing. The skin loses its ability to renew itself efficiently. Healthy cell function depends on adequate magnesium supply.
Inflammation And Allergies
Low magnesium can increase inflammation in the skin. This worsens conditions like eczema and dermatitis. Magnesium deficiency may also trigger allergy-like skin reactions. Redness, itching, and swelling become more common. Maintaining magnesium helps reduce these inflammatory responses.
Acne And Skin Appearance
Magnesium helps control skin inflammation that causes acne. A lack of magnesium can make acne worse and more frequent. The skin may appear dull, irritated, and uneven. Adequate magnesium supports clearer, healthier-looking skin by calming inflammation and improving overall skin quality.
Dietary Sources Of Magnesium
Magnesium plays a vital role in maintaining healthy skin. Getting enough magnesium through diet supports skin cell function and repair. It helps reduce inflammation and improves overall skin appearance. Consuming magnesium-rich foods can prevent deficiency and its effects on the skin.
Foods Rich In Magnesium
Nuts like almonds and cashews contain high magnesium levels. Seeds such as pumpkin and chia seeds are also excellent sources. Leafy green vegetables, including spinach and kale, provide magnesium. Whole grains like brown rice and oats contribute to daily intake. Beans and lentils add magnesium while offering fiber and protein. Dark chocolate with a high cocoa content contains magnesium too. Eating a balanced diet with these foods helps maintain healthy skin.
Supplements And Safety
Magnesium supplements offer an alternative to dietary intake. They come in various forms like magnesium citrate and magnesium oxide. Consult a healthcare professional before starting supplements. Taking too much magnesium can cause side effects like diarrhea or stomach upset. Follow recommended dosages to avoid risks. Supplements may help if diet alone does not meet magnesium needs. Regular monitoring ensures safe and effective use.

Credit: safehugs.in
Topical Magnesium Use
Topical magnesium use has gained attention as a way to support skin health. Applying magnesium directly to the skin is popular in baths, creams, and oils. Many people seek relief from skin issues through these products. Understanding how topical magnesium works can help set realistic expectations.
Benefits For Skin Conditions
Topical magnesium may reduce inflammation in the skin. This can help with eczema and psoriasis flare-ups. It might soothe itchy, irritated areas and improve skin comfort. Some users report faster wound healing after applying magnesium oils or creams. Magnesium also supports the skin’s barrier function, helping retain moisture. These benefits make topical magnesium a helpful option for some skin problems.
Limitations Of Absorption
Skin absorption of magnesium is limited and varies by person. The outer layer acts as a barrier, preventing full magnesium entry. Only a small amount penetrates deeply enough to affect cells. This makes topical magnesium less effective for fixing overall magnesium deficiency. Products may offer local relief but cannot replace dietary intake. For best results, combine topical use with magnesium-rich foods or supplements as advised by a doctor.
When To Seek Medical Advice
Recognizing when to seek medical advice for skin issues related to magnesium deficiency is important. Early consultation can prevent worsening conditions and guide proper treatment. Persistent skin problems may signal underlying health concerns needing professional care.
Signs That Require Medical Attention
Severe skin dryness, redness, or itching that does not improve needs a doctor’s evaluation. Slow healing wounds or unusual skin discoloration also warrant medical review. These symptoms might indicate a deeper magnesium imbalance or other health issues.
Skin Conditions Linked To Magnesium Deficiency
Conditions like eczema, dermatitis, and persistent acne may be connected to low magnesium levels. If these skin problems continue despite home care, medical advice is necessary. A healthcare provider can perform tests to confirm magnesium deficiency.
When To Consider Supplementation Under Supervision
Self-medicating with magnesium supplements can be risky without guidance. Doctors can recommend the right dosage based on your needs. They monitor for side effects and interactions with other medications during treatment.
Importance Of Professional Diagnosis
Skin symptoms can mimic other conditions unrelated to magnesium. A professional diagnosis ensures accurate treatment. Medical tests help identify if magnesium deficiency causes skin problems or if another issue exists.

Credit: safehugs.in
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Low Magnesium Affect Your Skin?
Low magnesium can cause skin thinning, slow wound healing, discoloration, and worsen inflammatory conditions like eczema and acne.
What Are The 10 Signs Of Low Magnesium?
Ten signs of low magnesium include muscle cramps, fatigue, nausea, loss of appetite, irregular heartbeat, numbness, anxiety, headaches, sleep disturbances, and muscle weakness.
Can Magnesium Cause Headaches?
Magnesium rarely causes headaches directly. Low magnesium levels can trigger headaches, but excess intake may also lead to them in some cases. Maintaining balanced magnesium supports headache prevention.
Can Magnesium Cause Bruising?
Magnesium rarely causes bruising directly. Low magnesium may impair healing, increasing bruise visibility. Consult a doctor if bruising worsens.
What Are Common Skin Problems Caused By Magnesium Deficiency?
Magnesium deficiency can cause thinning skin, slow healing, discoloration, and worsen eczema or acne.
How Does Low Magnesium Affect Skin Cell Function?
Low magnesium reduces energy for skin cells, causing poor regeneration and delayed wound healing.
Conclusion
Magnesium plays a vital role in keeping skin healthy and strong. Without enough magnesium, skin may become thin, slow to heal, and prone to inflammation. Many common skin problems like eczema and acne can worsen due to low magnesium levels.
Eating foods rich in magnesium helps support skin repair and reduce inflammation. Always talk to a doctor if skin issues persist or worsen. Proper magnesium intake protects your skin and promotes a clearer, healthier look. Taking care of your magnesium levels benefits your skin from within.
 Skip to content
Skip to content 