When you’re choosing colors for your projects, understanding the difference between pigment and dye can make all the difference in your results. You might think they’re just two names for the same thing, but they behave very differently and affect how your colors look and last.
Do you want vibrant, long-lasting hues that sit on top of your surface, or are you after translucent shades that blend smoothly into your material? Knowing these details can save you time, money, and frustration. Keep reading to discover how pigments and dyes work, so you can pick the perfect one for your next creative adventure.
Solubility And Composition
Understanding the solubility and composition of pigments and dyes helps reveal their core differences. These factors affect how each colorant interacts with materials and behaves in various applications.
Solubility refers to how well a substance dissolves in a liquid. Pigments and dyes differ significantly in this aspect. Composition relates to their chemical and physical makeup, influencing their stability and color properties.
Solubility Of Pigments
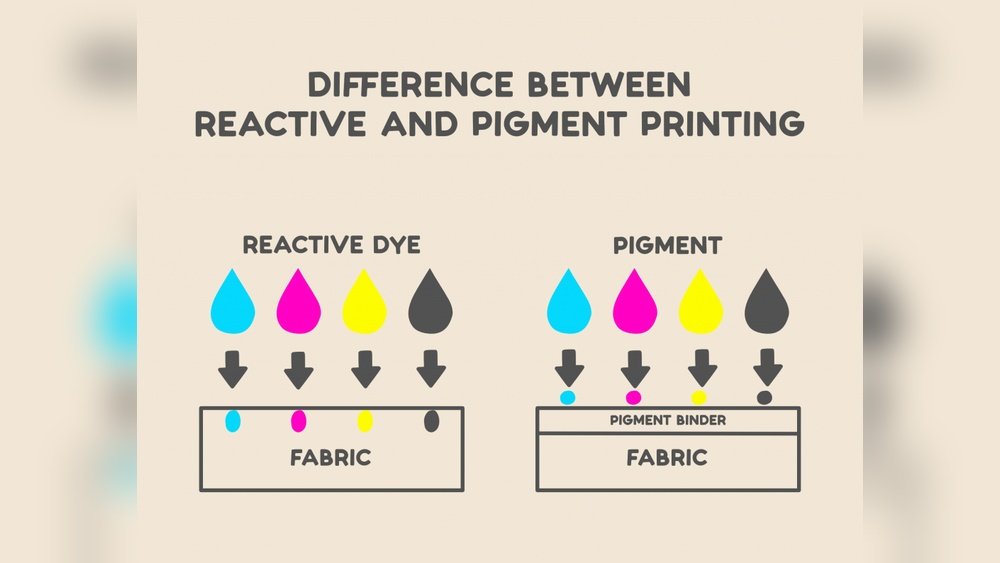
Pigments are mostly insoluble in water and other solvents. They do not dissolve but remain as tiny solid particles. These particles are suspended in a binder or medium to create color. Because they stay on the surface, pigments give a more durable and fade-resistant color.
Solubility Of Dyes
Dyes are soluble in water or organic solvents. They dissolve completely and penetrate the material they color. This ability allows dyes to bond chemically with fabrics or paper. The result is a vibrant, translucent color that soaks into the substrate.
Composition Of Pigments
Pigments consist of larger particles made from inorganic or organic compounds. They often contain metal salts or complex molecules. Their solid structure makes them stable under light and heat. This stability helps pigments maintain color over time.
Composition Of Dyes
Dyes are made of smaller molecules that easily dissolve. They are usually organic compounds with specific chemical groups. These groups form bonds with fibers or surfaces. Dyes can be less stable than pigments and may fade faster under sunlight.
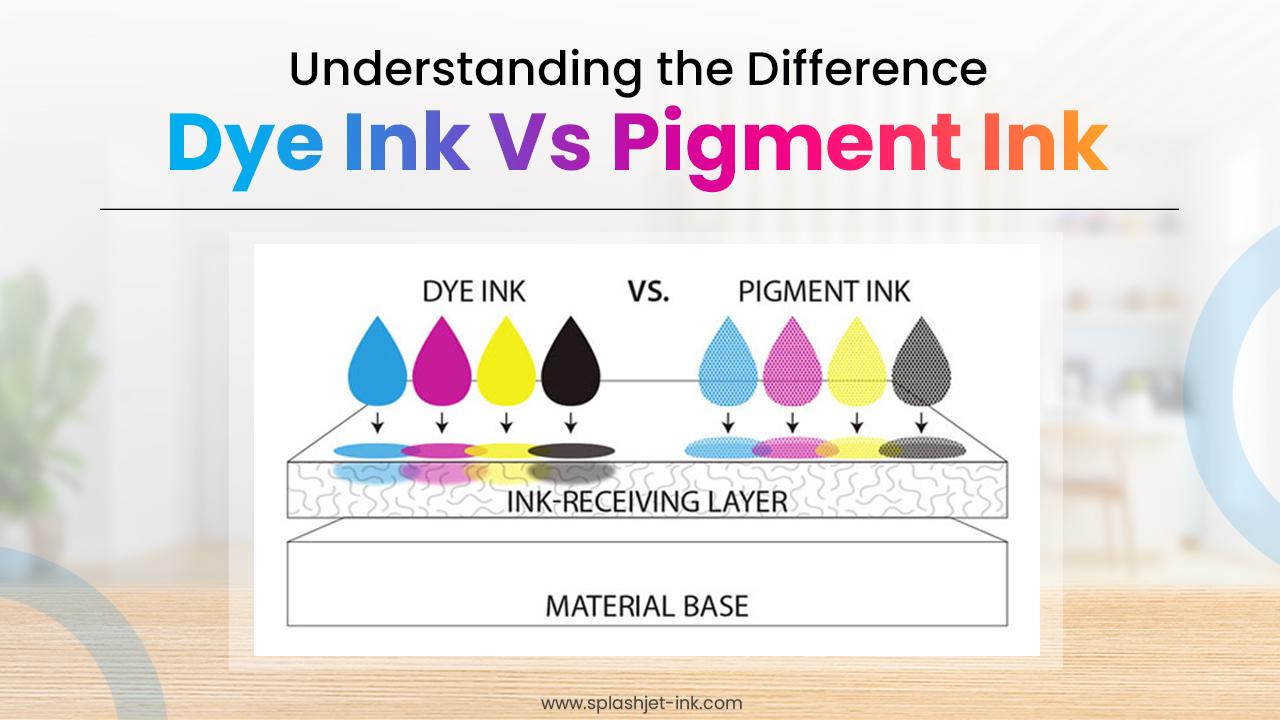
Credit: splashjet-ink.com
Color Vibrancy And Opacity
Color vibrancy and opacity define how pigments and dyes appear on surfaces. These factors affect the brightness and coverage of colors in various applications. Understanding their differences helps choose the right material for your project.
Color Vibrancy Of Pigments And Dyes
Pigments usually offer rich and intense colors. Their particles sit on the surface, reflecting light strongly. This creates bold and bright hues that stand out well.
Dyes dissolve into the material. They produce softer and more transparent colors. Dyes blend with the surface, giving a natural and smooth look.
Opacity Differences Between Pigments And Dyes
Pigments are opaque, meaning they block light from passing through. This quality makes pigments great for covering dark or uneven surfaces. They hide what is underneath clearly.
Dyes are mostly transparent or translucent. They allow light to pass, showing the material’s texture beneath. This makes dyes ideal for designs needing subtle color effects.
Application And Surface Interaction
The way pigments and dyes apply to surfaces and interact with materials differs greatly. These differences affect their use in art, textiles, and printing. Understanding these can help in choosing the right colorant for a project.
Pigments are made of tiny solid particles. They do not dissolve but stay on the surface. This makes pigments ideal for coatings that need to last long without fading.
Application Methods
Pigments usually require a binder or medium to stick to surfaces. They are mixed with oils, acrylics, or other substances. This mix forms a layer that remains on top of the material.
Dyes dissolve in liquids. They soak into the material deeply. This allows dyes to color fibers and papers evenly and smoothly.
Surface Interaction
Pigments create a film over the surface. This film blocks light and protects colors from washing away. They work well on rough or non-porous surfaces like metal and plastic.
Dyes penetrate the surface and bond with the material’s molecules. This results in vibrant colors that feel part of the fabric or paper. Dyes work best on porous surfaces like textiles and wood.
Durability And Resistance
Pigments resist water, sunlight, and chemicals better than dyes. Their particles do not change easily, keeping colors stable. This makes pigments perfect for outdoor paints and long-lasting prints.
Dyes can fade faster because they are sensitive to light and washing. They are less resistant to environmental factors. Dyes suit indoor items or projects requiring delicate, bright colors.
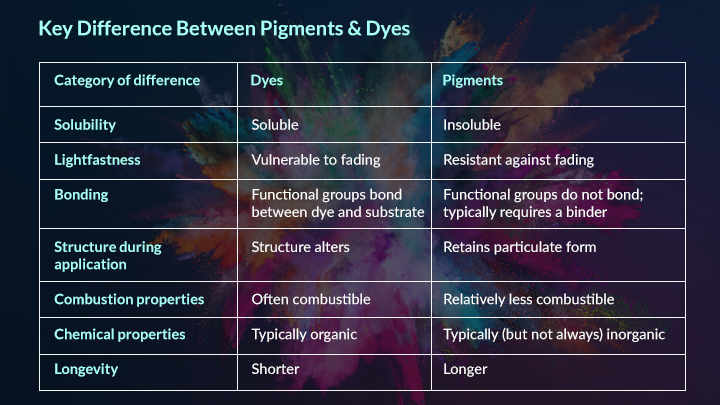
Credit: www.meghmaniglobal.com
Drying Time And Durability
Drying time and durability are key factors in choosing between pigment and dye. These qualities affect how the color looks and lasts on different surfaces. Understanding these differences helps in picking the right option for your project.
Drying Time Of Pigment Vs Dye
Pigment inks dry slower because the particles sit on the surface. They need time to bind with the material or medium. This slow drying helps pigments stay vibrant and sharp.
Dye inks dry faster as they soak into the material. The liquid evaporates quickly, leaving color inside the fibers. This quick drying suits fast projects and layered designs.
Durability Comparison
Pigments offer stronger durability. The color resists fading from light and water better than dyes. This makes pigments ideal for outdoor or long-lasting use.
Dyes are less durable. They can fade quicker when exposed to sunlight or moisture. Dyes work best for indoor projects or items not exposed to harsh conditions.
Effect Of Binder And Surface
Pigments need a binder to hold the color on the surface. This binder adds to drying time but increases resistance to wear.
Dyes penetrate fibers without a binder. This penetration helps the dye bond quickly but lowers resistance to rubbing and washing.
Best Uses And Suitability
Choosing between pigment and dye depends on your project needs. Each has qualities that fit certain uses better. Understanding their best uses helps you get the desired color effect and durability.
Best Uses For Pigments
Pigments work well for projects needing strong, lasting color. They are perfect for painting, printing on fabric, and outdoor applications. Pigments resist fading from sunlight and water. This makes them ideal for products exposed to weather. They also give a thicker, more opaque finish. Pigments suit surfaces like wood, plastic, and metal.
Best Uses For Dyes
Dyes work best for coloring materials by soaking into them. They are common in textile dyeing and paper crafts. Dyes produce bright, clear colors with a smooth look. They dry quickly and blend well with the material. Dyes suit fabrics like cotton, silk, and nylon. They also work well on light-colored surfaces for a soft, translucent effect.
Suitability Based On Material
Pigments suit non-porous and rough surfaces. They stay on top without soaking in. Dyes are better for porous and absorbent materials. They bond inside the material fibers. For example, pigment inks are great for dark paper, while dye inks work well on light paper. Choosing the right type protects your project’s quality and appearance.
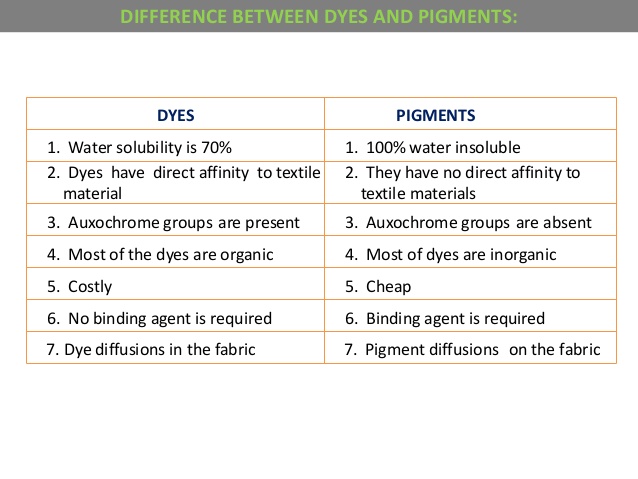
Credit: textiletools.blogspot.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Difference Between Pigment And Dye?
Pigments are insoluble particles that sit on surfaces, offering vibrant, fade-resistant colors. Dyes dissolve in liquids, soaking into materials for translucent, layered effects.
What Is The Difference Between Pigment And Dye Ink Pads?
Pigment ink sits on surfaces, offering vibrant, fade- and water-resistant colors, ideal for dark paper and embossing. Dye ink soaks into paper, dries fast, and creates translucent, layered effects, perfect for light cardstock and paper crafts.
Which Is Cheaper, Dye Or Pigment?
Dye is generally cheaper than pigment due to simpler production and solubility. Pigments cost more for durability and opacity.
How To Tell If Ink Is Dye Or Pigment?
Dye ink soaks into paper, appears translucent, and dries fast. Pigment ink sits on the surface, looks opaque, and resists fading and water. Test by rubbing water or light to check ink absorption and opacity.
What Is The Main Difference Between Pigment And Dye?
Pigments are insoluble particles, while dyes dissolve completely in liquids.
How Do Pigments And Dyes Affect Color Fastness?
Pigments are more fade-resistant; dyes tend to fade faster under sunlight.
Which Is Better For Fabric Coloring, Pigment Or Dye?
Dyes penetrate fabric fibers; pigments sit on the surface, affecting durability.
Conclusion
Pigments and dyes differ mainly in how they color materials. Pigments do not dissolve; they sit on surfaces and resist fading. Dyes dissolve and soak into materials, offering bright but less lasting colors. Both have unique uses depending on your project needs.
Understanding their differences helps you choose the right one. This knowledge improves your results whether crafting or working professionally. Keep these points in mind for better color choices every time.
 Skip to content
Skip to content